Hand and finger infections are mostly caused by injuries such as needles, splinters, or injuries that we don't pay attertion. Hand and fingers are separated by various boundaries. Infections that reach these areas through open injuries or foreign objects cause localized or widespread infections. Infections agents are mostly bacteria, and rarely fungi or viruses. Most of these agents are on the skin of the healthy person's hand and injuries, deterioration in the integrity of the skin due to being constantly wet helps them to move from the surface of the hand to the interior.
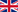
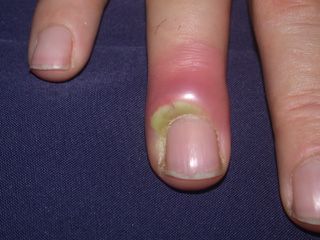
Panaris (nail side infection), paronychia (inflammation of the nail root) and felon (inflammation of the pulp-finger touch surface) are the most common soft tissue infections of the fingers and hand.(Figure 1.2)